I recently talked about tools that promise to measure the visibility on Google AI Mode, ‘VE Overviews and the LLM. I explained why I couldn’t see no urgency to subscribe to it, and why I expect data instead IA native in Search Console, especially in France, where these features are not yet active.
A recent study shows variation between some of the data API used by these tools, and the answers actually displayed.
This is where it gets interesting.
Dans cet article
AI hates bullshit
First find (a bit anecdotal, but talking) : AI hate the bullshit.
The long intros, the excess of details, the jargon and useless, and all that, it is necessary to forget.
It worked at the time of the Helpful Content Update from Google, but Google has let go of the case. Today, it is necessary to go right to the goal.
Thus entering the heart of the matter !
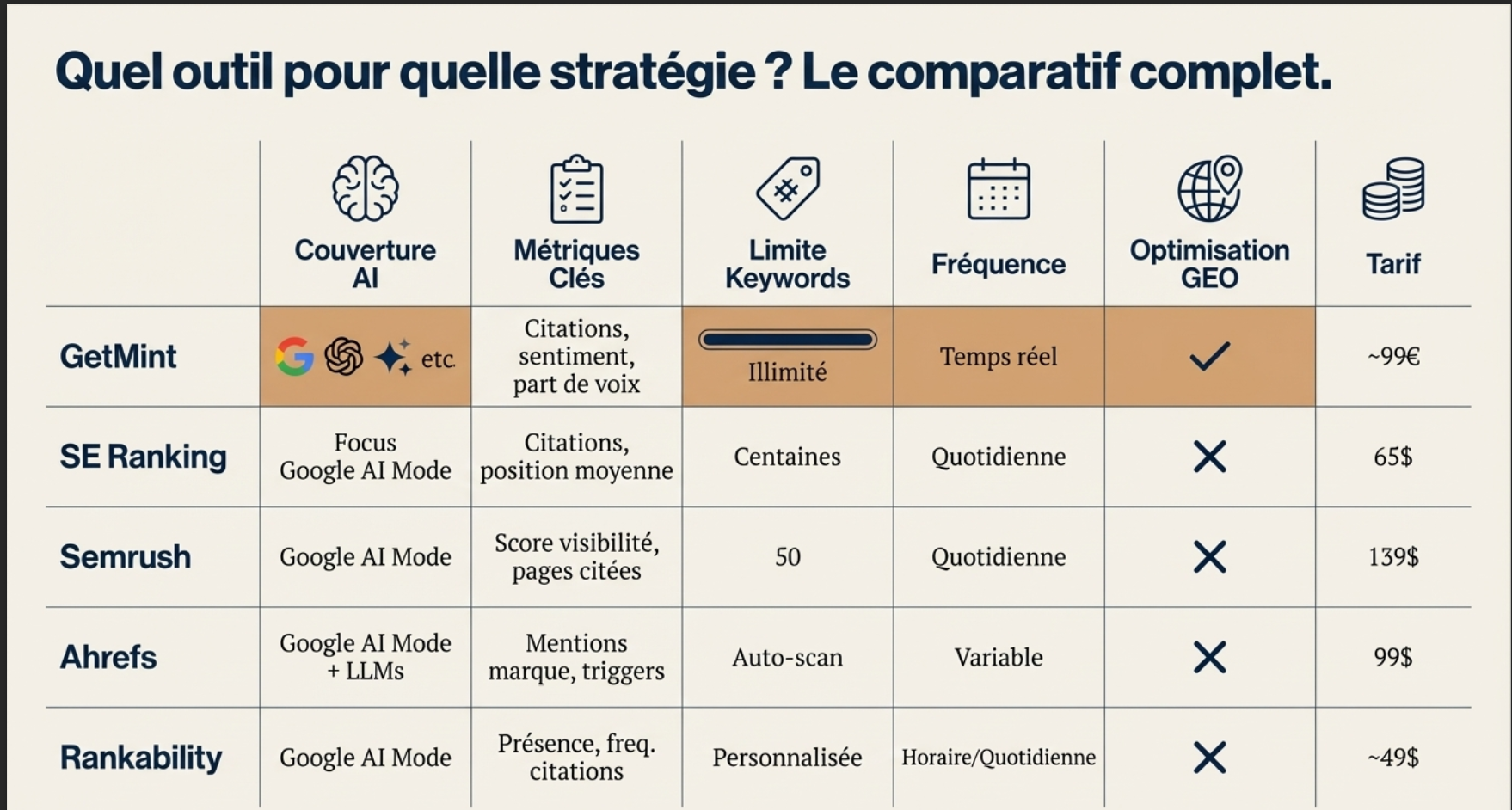
The responses generated by the AI by scraping vs results API. What are the differences ?
The study mentioned above was carried out by Surf Blog, that I did not know before. The results, however, are very interesting.
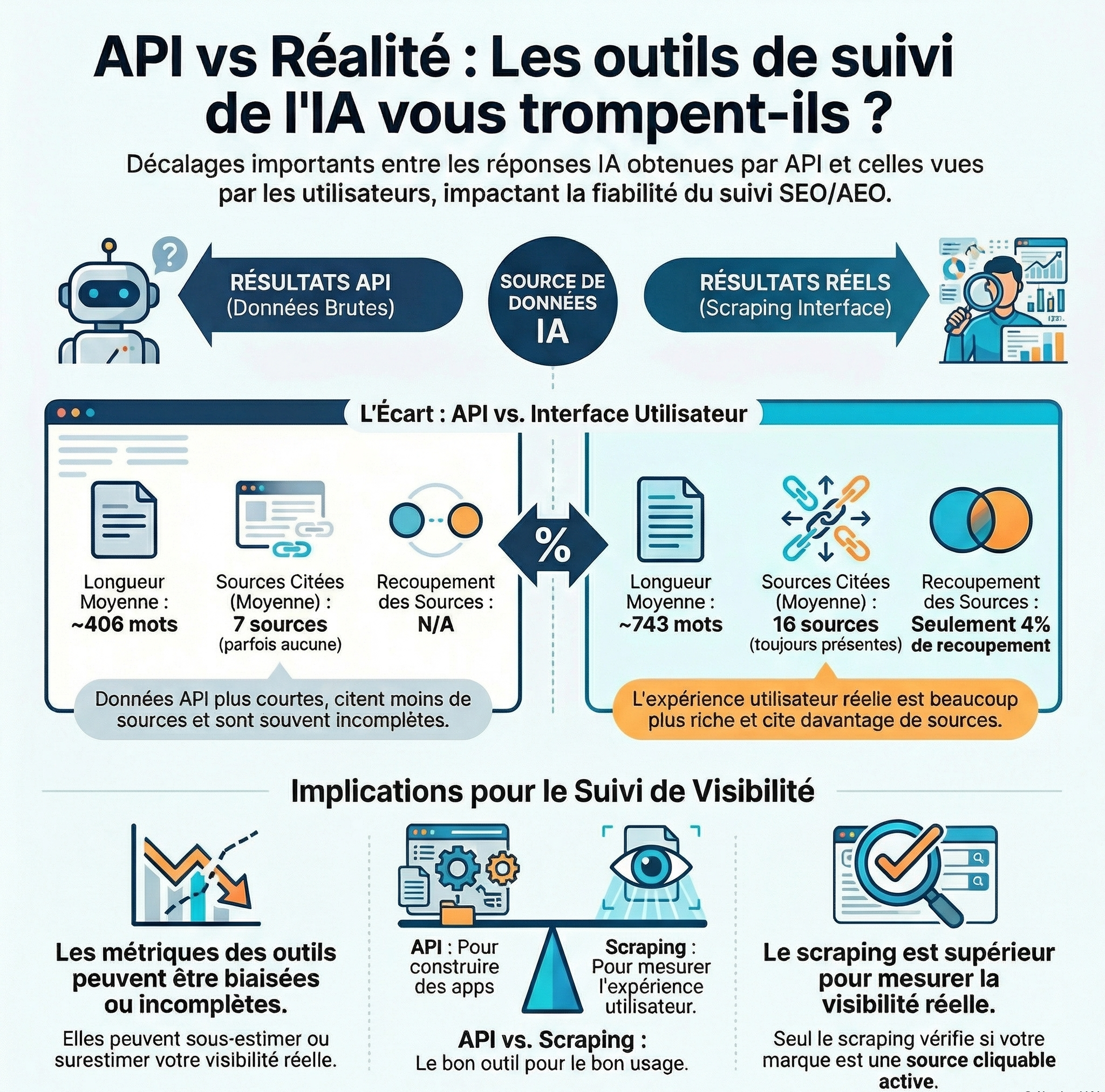
Here are the main findings in the form of a table :
| Aspect | Results API | Actual results (scraping) | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Answer length | ~406 words average | ~743 words average | The responses APIS are often shorter and less detailed than what actually sees the user |
| Triggering Web Search | ~23 % of the responses do not trigger the research, especially if <100 words | Still triggered | The answers scrapées contain more sources and more diversified |
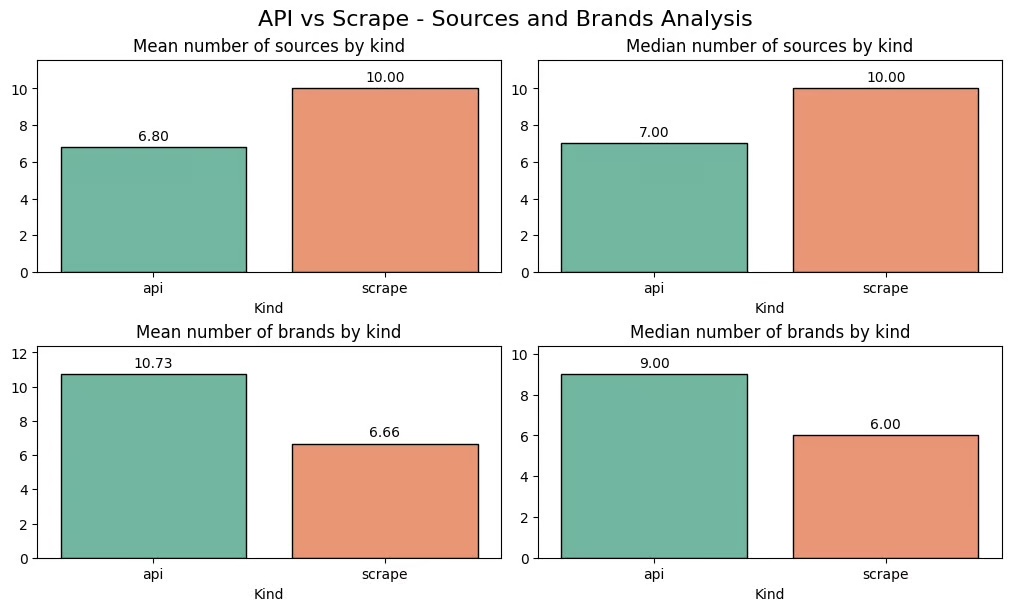
| Sources cited | No source in ~25 % of cases ; average 7 sources | Always present ; average of 16 sources | The real answers provide nearly two times more sources |
| Detection of brands | 8 % of the responses’t detect any brand ; an average of 12 marks when there are | Always detected ; average of 9 marks | The API detects, on average, more marks per answer, but misses some |
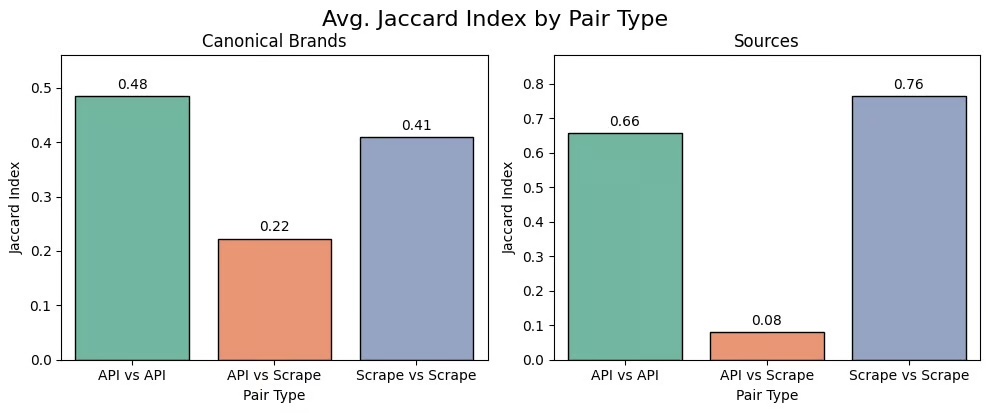
| Overlap API vs scraping | — | — | Only 24 % marks and 4 % of the sources overlap between API and scraping |
| Overall summary | Data in a more structured, shorter, sometimes incomplete | Data longer, complete, with the logic of the interface and all the sources | To build apps : API → ideal ; to monitor the real-life experience : scraping → vital |
Chatgpt :results API vs actual results
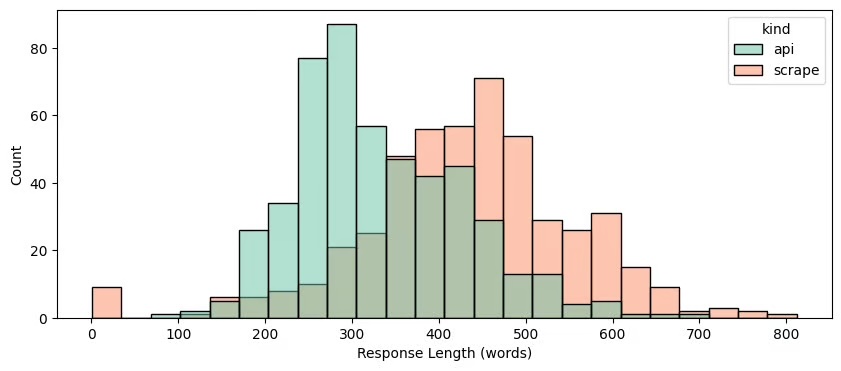
Surf has been compared to approximately 2,000 queries : the same question asked in ChatGPT (and Perplexity) via API vs. the answers actually displayed to a user (scrap). And the differences are substantially important.
Length of answers API vs actual results
- API : ~406 words average
- Scrap real : ~743 words average: APIS often involved in responses shorter and less detailed than what the user really sees.
The responses from the API are significantly shorter than those retrieved via the interface.
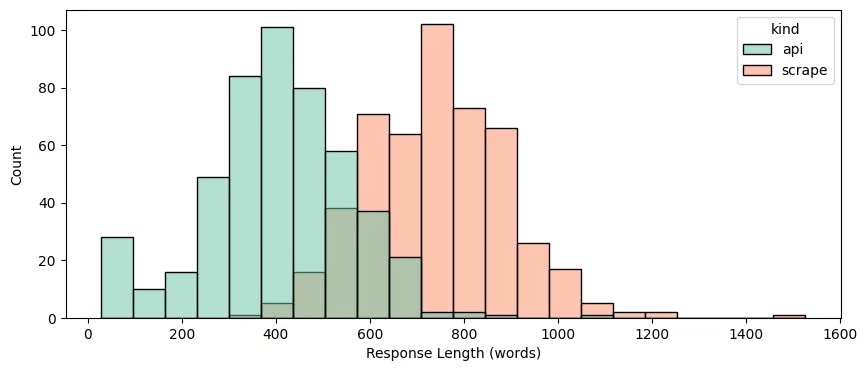
Triggering of the Web search API vs actual results
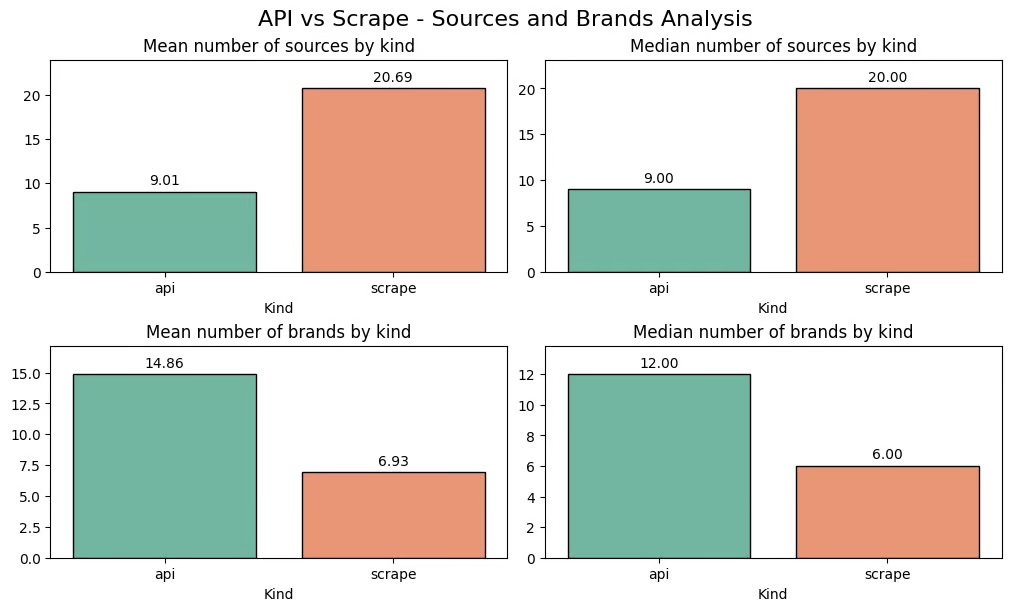
- In ~23% of the cases, the API does not trigger Web search so that the real answers are.
- The answers “scrapées” contain more sources cited and most diverse in the API.
About 23 % of the responses API will not initiate research on the Web, usually when they are less than 100 words. In contrast, responses recovered trigger a systematic search.
Sources answers results API vs actual results
The API does not provide any source in approximately 25 % of cases. The responses generated by theAI from data scrapées always provide sources, and about two times higher (16 vs. 7 on average).
Detection of brand results API vs actual results
The data from the API does not detect any trademark in about 8 % of the cases, while the responses retrieved identify still brands.
When a mark is detected, the API identifies on average more : 12, against 9.
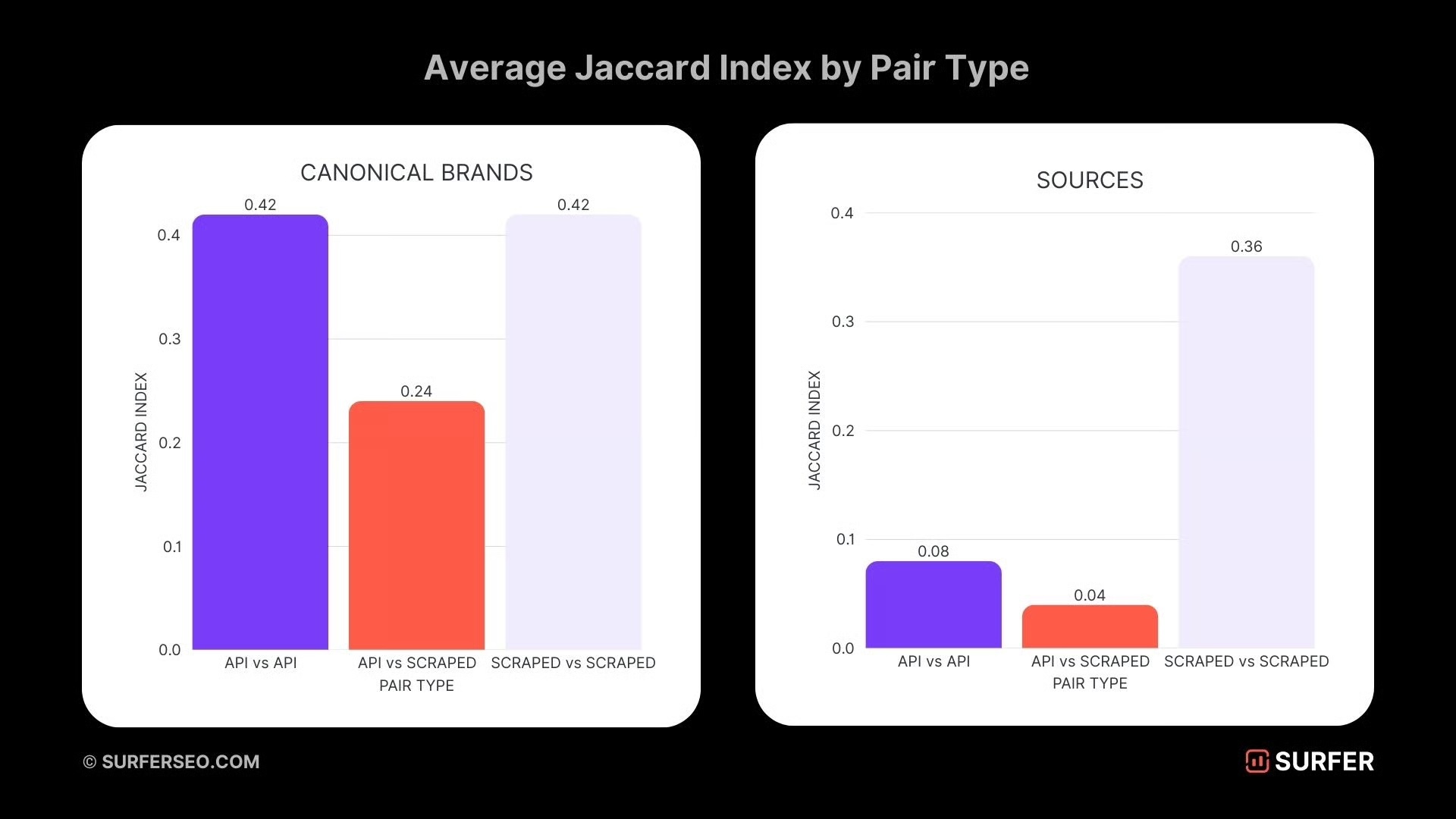
The results API and the results ChatGPT are they the same ?
Then, the results are they the same results with the API and the web interface/app ?
The answer : no, absolutely not.
The differences are striking :
- Only 24 % of marks detected overlap between the API and the scraping.
- For the sources, the overlap drops to only 4 %.
Okay, we have seen the difference between the responses recovered by scraping on ChatGPT and those provided directly by the API. Now let’s see what gives Perplexity.
Perplexity : the differences between the results recovered by scraping and those obtained via the API
| Aspect | Results API | Retrieved results (scraping) | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Answer length | ~332 words | ~433 words | The answers API are shorter and less detailed |
| Web Search | Still used, but some sources may be omitted, sometimes leading to the complete lack of response | Always used, all sources | The scraping reflects the actual experience of the user |
| Sources cited | Average 7 | 10 | The responses extracted contain systematically sources |
| Mentions of brands | Typically more than 10 marks | Approximately 6 marks ; 5% of the responses replace the name of the generic job descriptions | The answers API to identify more brands, but some of the answers extracted are more accurate |
| Overlap API vs scraping | — | — | Only 8 % of the sources overlap between the API and the scraping, showing references are often different |
Length results recovered by scraping and those obtained via the API
The answers API are shorter, with an average of 332 words, against 433 words for the answers retrieved.
Web search : results recovered by scraping and those obtained via the API
The two methods always use the Web search, but the API can sometimes omit some of the sources, which can lead to the total lack of response.
Sources : the results recovered by scraping and those obtained via the API
The API return on average 7 sources, while the responses retrieved by always contain 10.
Mentions of brands : results recovered by scraping and those obtained via the API
In about 5% of the responses extracted, the brand names are replaced by descriptions more generic. The answers API generally include more than 10 brands, compared to about 6 for the answers extracted.
Trademarks and sources are similar in Perplexity ?
Again : NO.
The overlap of sources nis 8 %, which means that theAPI and theuser interface soften rely on references that are totally different.
What it wants to tell on the reliability of tracking tools
The majority of the tools of visibility IA is based on the API of the LLMs to extract metrics (such as frequency of mentions, presence in LLM, visibility, etc). But the study shows that these APIS are not intended to reflect not accurately reflect what the users actually see in the interface of the LLMs (ChatGPT, Perplexity, etc).
This means that :
- The metrics of tracking may be biased or incomplete
- They may underestimate or overestimate the real visibility
- They may poorly represent the way in which a mark or website is referred to in the responses visible
In short : use the API as a unique proxy to measure the visibility IA/LLM is, according to this study, insufficient or even misleading, which explains your distrust vis-à-vis these tools.
Why theAPI seems to be less efficient (and why cis wrong) ?
An article of Gumshoe I attack the idea that APIS are the de facto less efficient. According to him, the gap between the API and the UI is mostly the lack of system prompts (system messages).
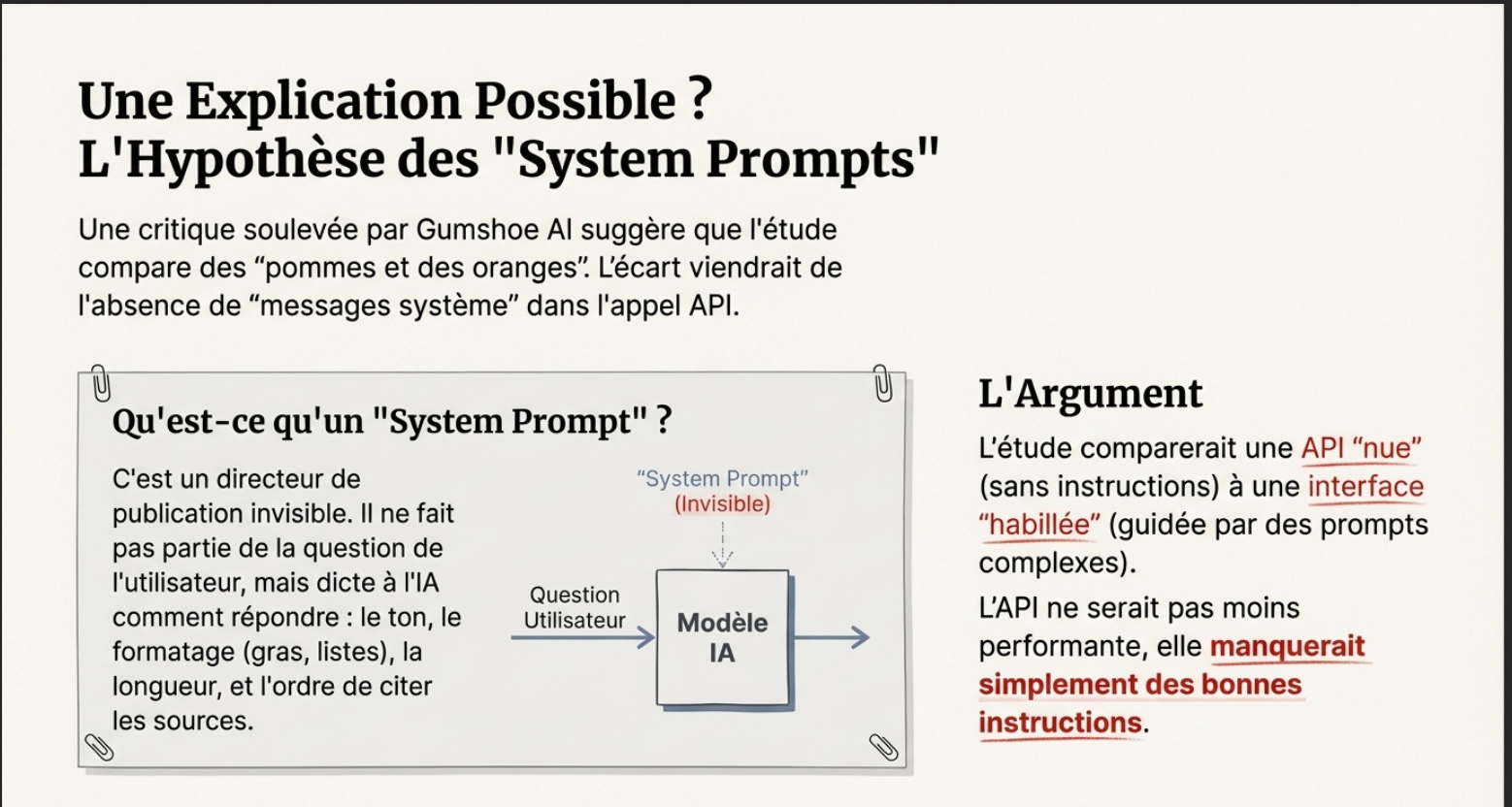
The Role of the ‘System Messages’
System messages work as a director of publication invisible : they are not part of the question of the user, but dictate the AI how to respond. They control :
- Citations : in order to quote sources.
- Length : verbose or concise (where the raw API often shorter).
- Formatting : bold, lists, tables…
Gumshoe’VE been trying to convince us that thestudy of SurferSEO comparing apples and oranges :
- They compare an API ‘naked’ (default settings, no instruction behavior).
- To an Interface ‘dressed’ (strongly guided by prompts system-complex).
For him, the API that forgets citations or trademark that is not less powerful : it just lacks good instructions.
Except… SurferSEO has used a model with a system prompt. So yes, interesting article, but perhaps it is not that the true variance.
they say black and white :
We tested two scenarios, by running 1 000 requests every time.
Surfer SEO
Atfirst, we compared the results obtained with thehelp ofan API ‘ clean ‘.
Then, we’ve added a twist : we used a system prompt OpenAI released on GitHub.
The results were almost identical in the two cases, with and without thesystem prompt.
Two tested scenarios :
- Scraping IU vs API “clean”
- It is compared that the UI displays with what the API returns by default, without additional instructions.
- Objective : to measure the difference in baseline between UI and API.
- Scraping IU vs API with system prompt
- It adds to the API, a system prompt OpenAI disclosed.
- Objective : to see whether it brings the results of the UI.
Result : in both cases, the results were almost identical. The gap does, therefore, not necessarily of the system prompts.
API OpenAI vs ChatGPT : what is the difference ?
ChatGPT, this is the model(API) gross more :
- special instructions (system prompt),
- flow of additional data,
- a logical interface,
- and a few adjustments secrets known only to OpenAI.
These layers are as ChatGPT behaves differently from the API, even with exactly the same model.
Difference between collecting responses via API VS collecting responses via scraping
| Aspect | Web Scraping | API Access |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Capture the real experience of the user | Access data in a structured and programmatic |
| Includes | – Final Message displayed to the user – formatting – interactive Elements of the interface – Sources – additional Logic applied by the platform | – Own response and structured – Call functions – Formats consistent |
| Does not provide | Data Structure ready to use | Interface, behavior research, the sources, the “magic” added |
| Recommended use | Monitor how your brand or your content appear in the tools did | Build apps, automate treatments or integrations |
If you want to understand the differences between these two methods of data collection and their issues, I recommend the article SEO Clarity, that explains them in detail.
Verdict ?
For the team of SEO clarity, when itis of GEO, the Scraping ofthe Interface is higher.
Why ? Because theAPIS lack of nuance. In the research, IA, the visibility depends not justbe mentioned in the text, but tobe cited as a source clickable. Only the scraping allows you to check if your brand is presented as a recommendation active, with a link, or simply as a word in a paragraph of plain text.
In summary : theAPI is ideal for data clean and fast on a large scale, but it is blind to theuser experience for real. To understand your true visibility in theIA, you must see what theuser sees, and only the scraping allows.
The difference between responses API vs real answers on Google AI Overviews
Google and its solutions AI are not immune to the debate on the differences between responses and API responses ‘ real ‘. Explanation :
Writesonic has published an excellent article that highlights the differences between the responses provided via the API, and publicly accessible in the ecosystem Google.
The finding is in line with that of SEO Surfing : what tools GEO see through the API is often not what your customers see on their screen.
API : it is often based on classification methods conventional and index sometimes less-to-date. It returns the raw data, structured but incomplete side ‘ generated response ‘.
IU (human vision) : it uses LLM, which summarize the information in real-time, offering a response rich, contextual, and personalized
The 4 Reasons of the Discrepancy
Writesonic identifies four key factors that explain why the API and the UI does not give the same results :
- Different algorithms : the API is often based on conventional criteria (backlinks, keywords), so that the UI uses LLM to synthesize a relevant answer, not just to classify the links.
- Freshness of the data (AAR) : the UI can look up information in real time through the RAG, where the API is based on the index static updated less often.
- Customization & context : the UI takes into account the history, the location and the previous queries. The API, it remains ‘ cold ‘.
- Post-processing : the UI clean, and writes the results to avoid duplication and bias, which is not done to the raw data from the API.
My opinion on the difference between the responses LLM API vs the results LLM scrapees
Honestly, it does not surprise me. In my SEO audits/GEO, I often see that the answers API does not stick to the scraping reveals.
To be clear : the API is scalable and safe, but it does not reflect the real experience. The UI shows the reality, but it is more complex and sometimes risky.
Personally, all this debate is that give me even more eager to explore the data IA directly via Search Console…
Sources
The quality source cited in this article are collected here :
- https://surferseo.com/blog/llm-scraped-ai-answers-vs-api-results/
- https://blog.gumshoe.ai/how-apis-unlock-better-insights-into-ai-search-visibility/
- https://writesonic.com/blog/api-vs-ui-results
Leave a Reply